Scoliosis
Scoliosis
What is Scoliosis?
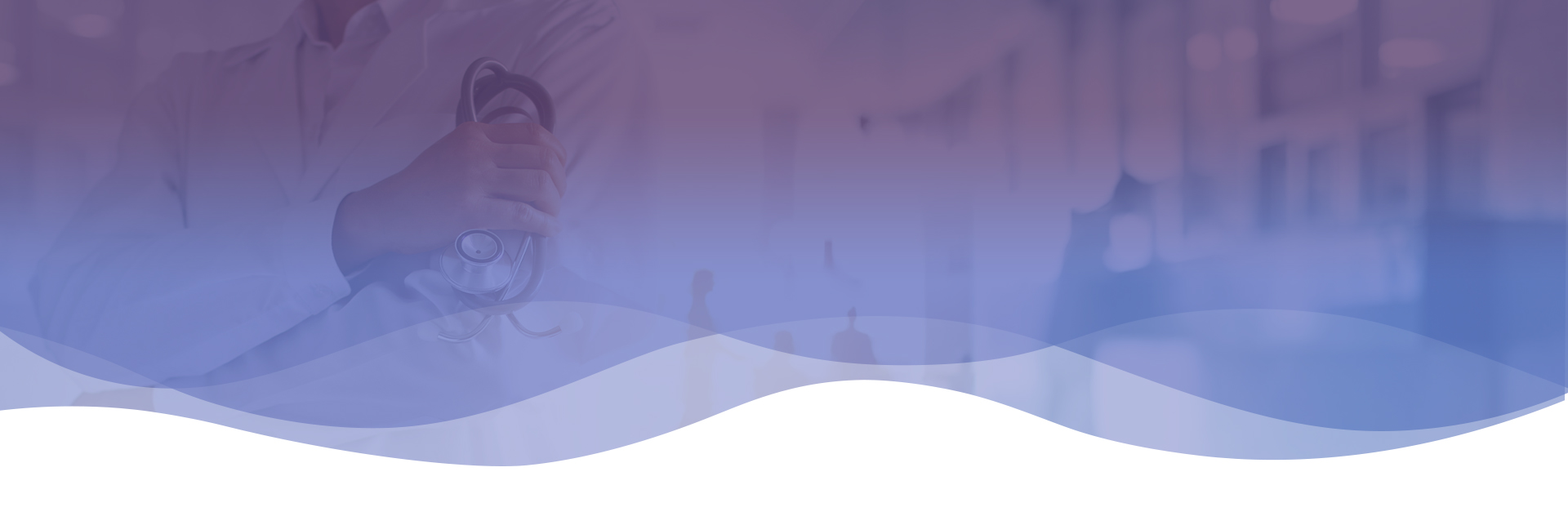
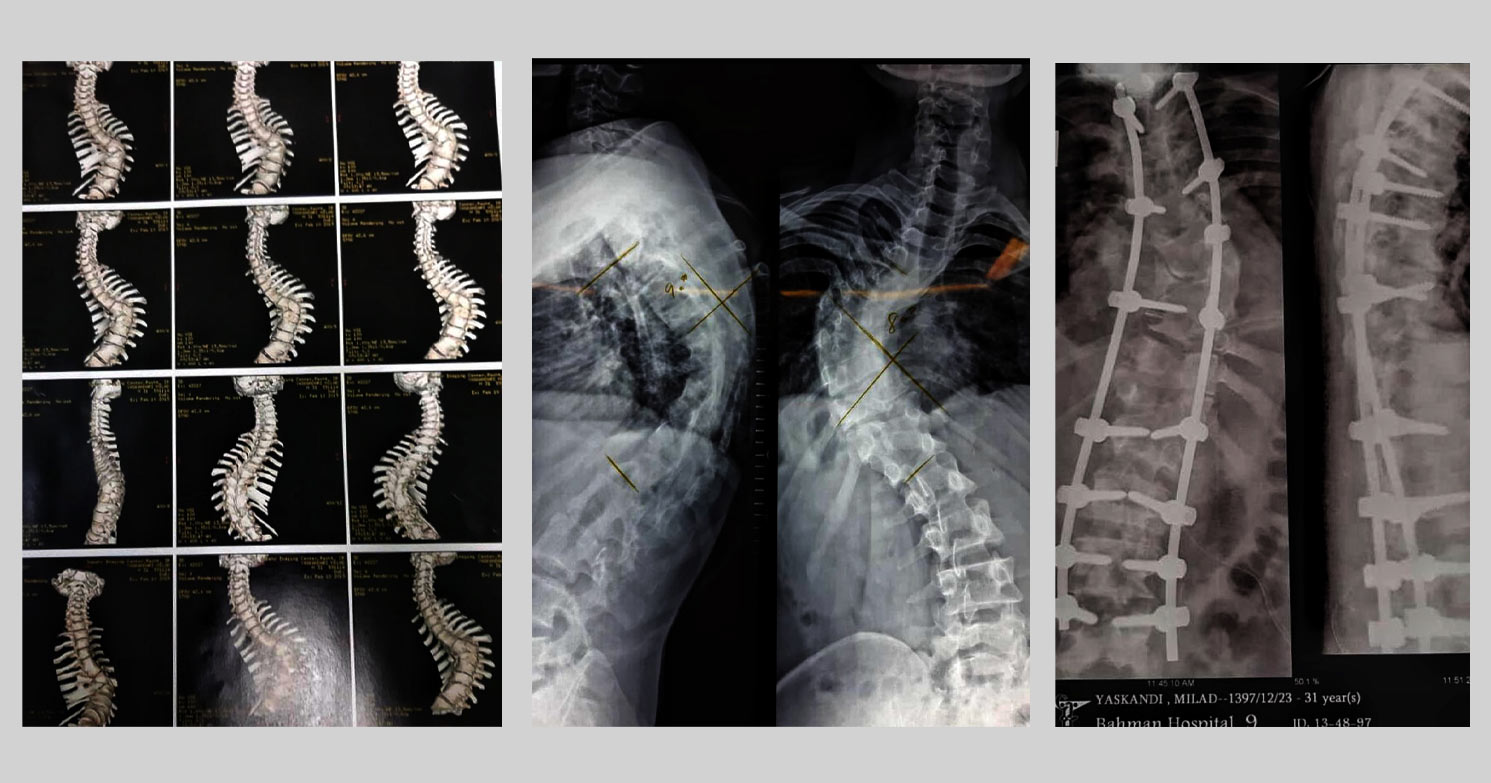
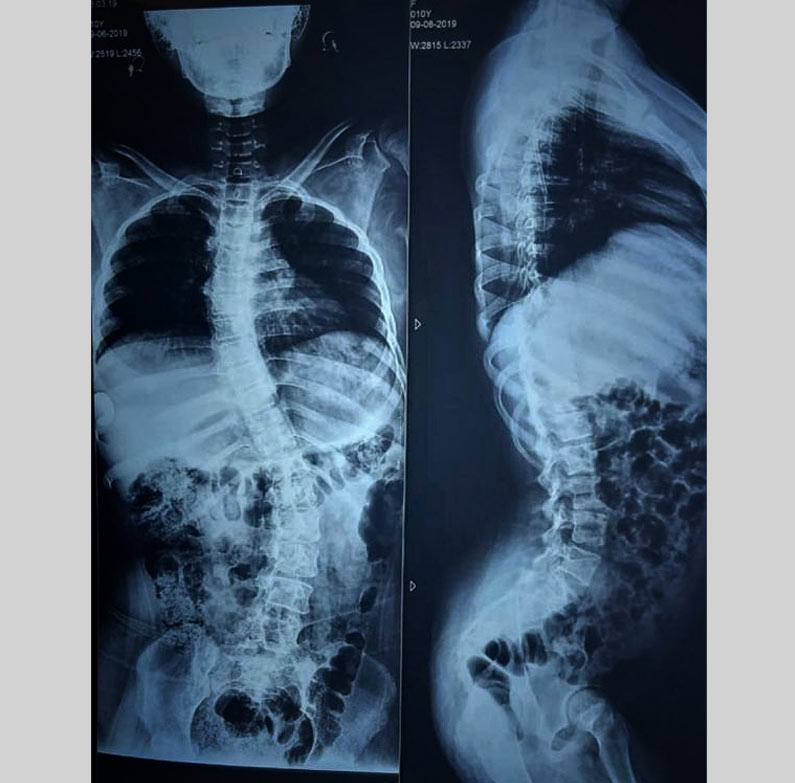
Scoliosis is a condition of side-to-side spinal curves. On an x-ray, the spine of a person with scoliosis looks more like an “S” or a “C” than a straight line. These curves can make the person’s shoulders, hips or waist appear uneven. In scoliosis, the spine’s vertebrae may also be rotated, causing one shoulder blade or trunk muscles to be more prominent than the other.
Scoliosis does not result from carrying heavy items, sports, poor posture, or minor leg length abnormalities. In fact, in more than 80 percent of scoliosis cases, a specific cause is not known. Such cases are termed idiopathic (meaning of undetermined cause), and they are most commonly found in adolescent girls.
Infantile idiopathic scoliosis is found in children ages 0 to 3.
Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis is found in in children ages 4 to 10.
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is found in adolescents ages 11 to 18.
Adult idiopathic scoliosis is found in patients older than 18.
Less often scoliosis develops in those diagnosed with other conditions.
Neuromuscular scoliosis is associated with diseases like cerebral palsy (CP), spinal muscle atrophy (SMA), Angelman syndrome, Arnold-Chiarimal formation/syrinx or trauma to the spinal cord.
Syndromic scoliosis is related to other diseases:
1-Myopathic (muscular system-related) disorders like muscular dystrophy, poliomyelitis, arthrogryposis or spinabifida;
2-Connective tissue diseases (Marfan syndrome and Ehlers-Danlossyndrome);
3-Genetic conditions (osteochondrodystrophy [dwarfism], Noonansyndrome, neurofibromatosis), and certain syndromes related to multiple birth defects like VATER syndrome.
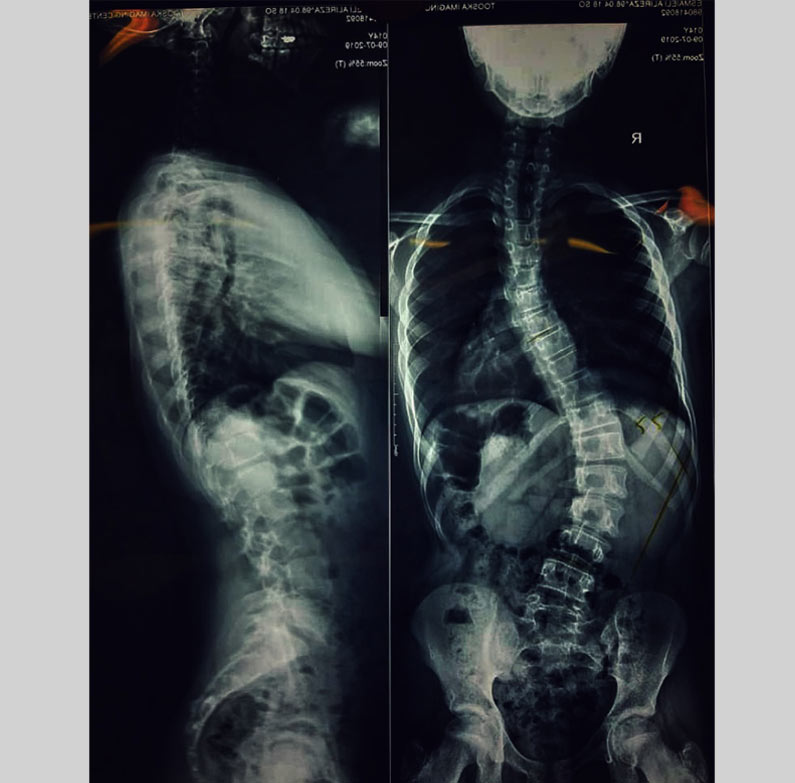
Congenital Scoliosis
Spinal cord deformity in early fetal weeks cased Congenital scoliosis that is more common in girls than boys.
Scoliosis symptoms
1-Spinal deformation
2- Limbs Asymmetry
3-Sagital imbalance
4-Pressure on inner chest organs like heart and lungs
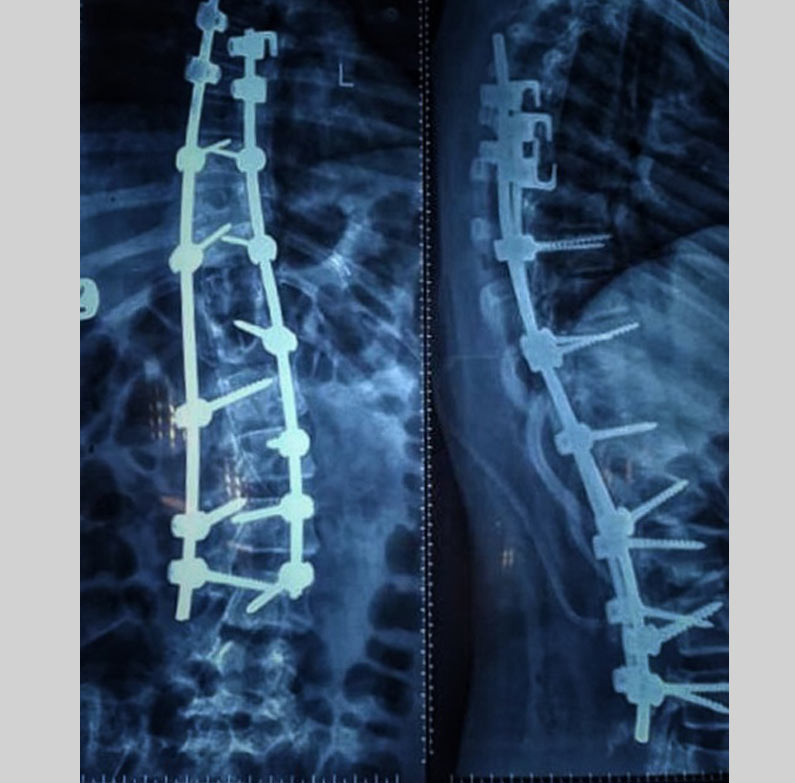
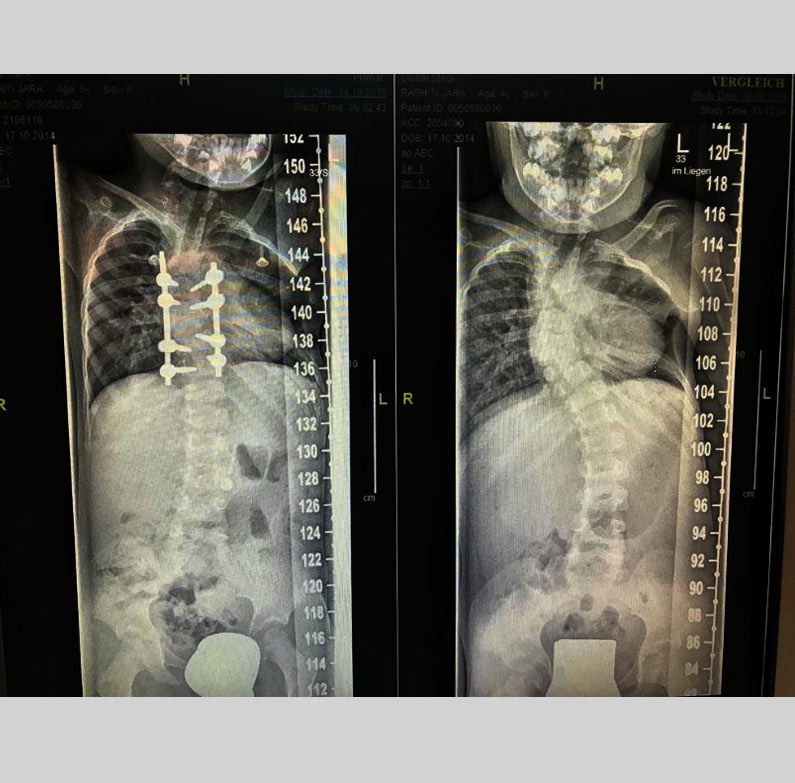
Treatment options
1-Non-Invasive
2-Invasive(Surgical)
Non-invasive:
Primary treatment for Scoliosis are non-surgical treatments like: Brace halo-Orthese-Traction-Physiotherapy.
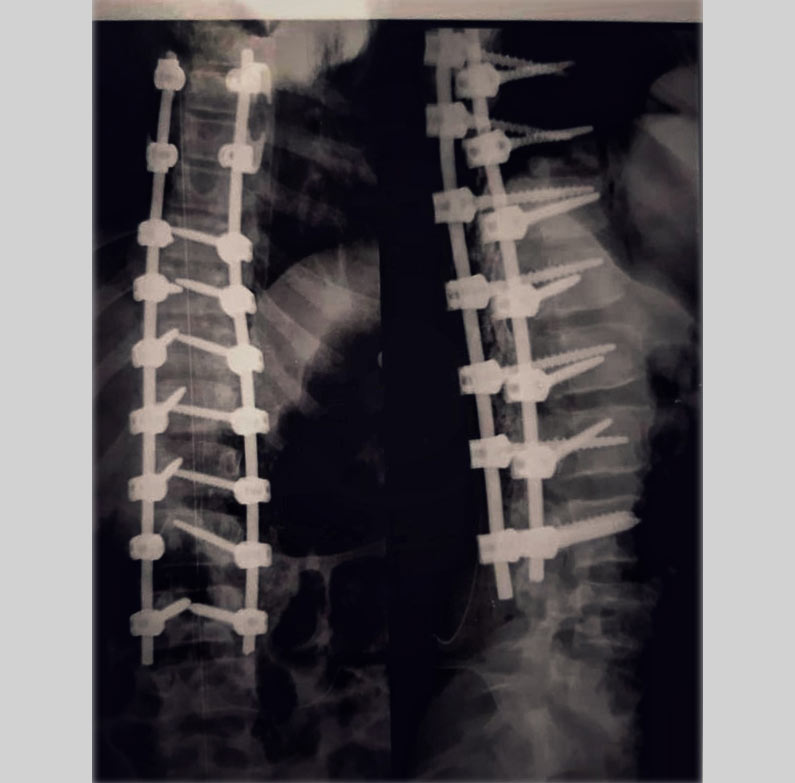
Surgical:
For widening spinal cord, some surgical procedures have to be performed, that depends on patients conditions.
Laminectomy: removal Lamina bone to relieve spine canal stenosis.
Disectomy: Removal of abnormal disc.
Corpectomy: Removal total or a part of vertebral body.
Fusion: Fusing two or more vertebrae.
SRS.ORG :References